CIPS L6M5 Übungsprüfungen
Zuletzt aktualisiert am 25.04.2025- Prüfungscode: L6M5
- Prüfungsname: Strategic Programme Leadership
- Zertifizierungsanbieter: CIPS
- Zuletzt aktualisiert am: 25.04.2025
Spaceman Ltd’s R&D team has a strong relationship with its supplier of spaceship parts.
The space exploration industry is becoming highly competitive.
The team is looking for ways to enhance profits and market share.
Q: What strategy should Spaceman Ltd use? Answer Options:
- A . Variance Analysis
- B . Value Engineering
- C . Consortium-Based Procurement
- D . Open-Book Costing
Golden Rainbow Ltd has invested £4m in a new research project started three years ago. The CFO calculates that the average rate of return on the project is C6%. Is this possible?
- A . yes C projects can have a negative rate of return
- B . yes C but this is likely to change to a positive figure shortly
- C . no C a rate of return is always displayed as a positive number
- D . no C a rate of return is expressed in years rather than as a percentage
Which of the following is true about Engineering, Procurement, and Construction (EPC) Contracts? (Select all that apply.)
EPC contracts, commonly referred to as Turnkey Projects, are widely used in construction and infrastructure projects. These contracts require the contractor to design, procure materials, and construct the project to deliver a complete and operational facility to the client. Answer Options:
- A . The contractor is responsible for the design aspect of the construction
- B . The contractor may operate the building for a certain period after completion
- C . These contracts are commonly known as Turnkey Projects
- D . These contracts are sometimes referred to as Design and Build Contracts
- E . These contracts are used when forming a partnership between a private and public organization
Skipped
Which of the following statements is true of a business that operates in a ‚low-context culture‘ country?
- A . Employees are more loyal
- B . Religion is not important
- C . Communication is direct and meetings are therefore shorter
- D . There is a blending of work and home life
Which of the following statements about liquidated damages are TRUE? Select all that apply
- A . a set figure is decided in advance
- B . the figure must be a genuine estimate of the loss
- C . the party seeking damages must prove the actual loss in the event of a claim
- D . liquidated damages can be claimed when a warranty is breached
- E . specific performance is a type of liquidated damage
"Persuasion should be a last resort in cultural change." Is this statement true? Answer Options:
- A . Yes C persuasion should be linked to an implicit or perceived threat
- B . Yes C persuasion should only be used after coercion has failed
- C . No C persuasion should be planned before implementing change
- D . No C persuasion is not useful in large cultural shifts
The Human-Relations Model describes a type of organization with a set of values.
Which TWO of the following apply?
- A . high levels of flexibility
- B . low levels of flexibility
- C . a focus on internal business functions
- D . a focus on the external environment
Which type of organisational culture has a flat hierarchy and a fast responsiveness to change?
- A . power
- B . task
- C . role
- D . person
Scenario:
Fin Inc is a consultancy organisation in the private sector, founded 10 years ago by CEO Geoff Davies, who runs a tight ship. Many employees are scared of Geoff, and there are rumours that he fires people for refusing overtime. Fin Inc is working with a new client on a shopping centre project led by the well-liked CFO. The client wants a flexible, collaborative contract with transparent cost-sharing.
What type of organisational structure does Fin Inc have?
- A . power
- B . role
- C . task
- D . person
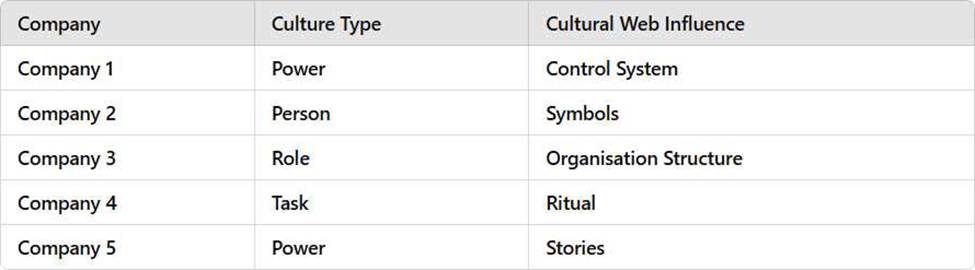
DRAG DROP
Below are descriptions of five companies in the UK. Each company has a unique organisational culture and a key Cultural Web Influence that shapes its structure and operations.
Your task is to match the correct type of organisational culture and cultural web influence to each company.
Company Descriptions
Company 1
Description: Authority is centred around the founder. There are strict financial systems and a
reward/bonus scheme for meeting targets.
Company 2
Description: Employees operate independently and often bring in their own clients. There is a strong
corporate identity and branding.
Company 3
Description: Strict hierarchy determines salary and job titles. The organisation is described as
bureaucratic and follows stringent rules.
Company 4
Description: Employees work in small teams or individually on projects. There is a strong emphasis on weekly team meetings where tasks for the upcoming week are discussed. Company 5
Description: Authority is held by senior leadership who make all decisions. There are few rules, and culture is reinforced by storytelling about past successes.